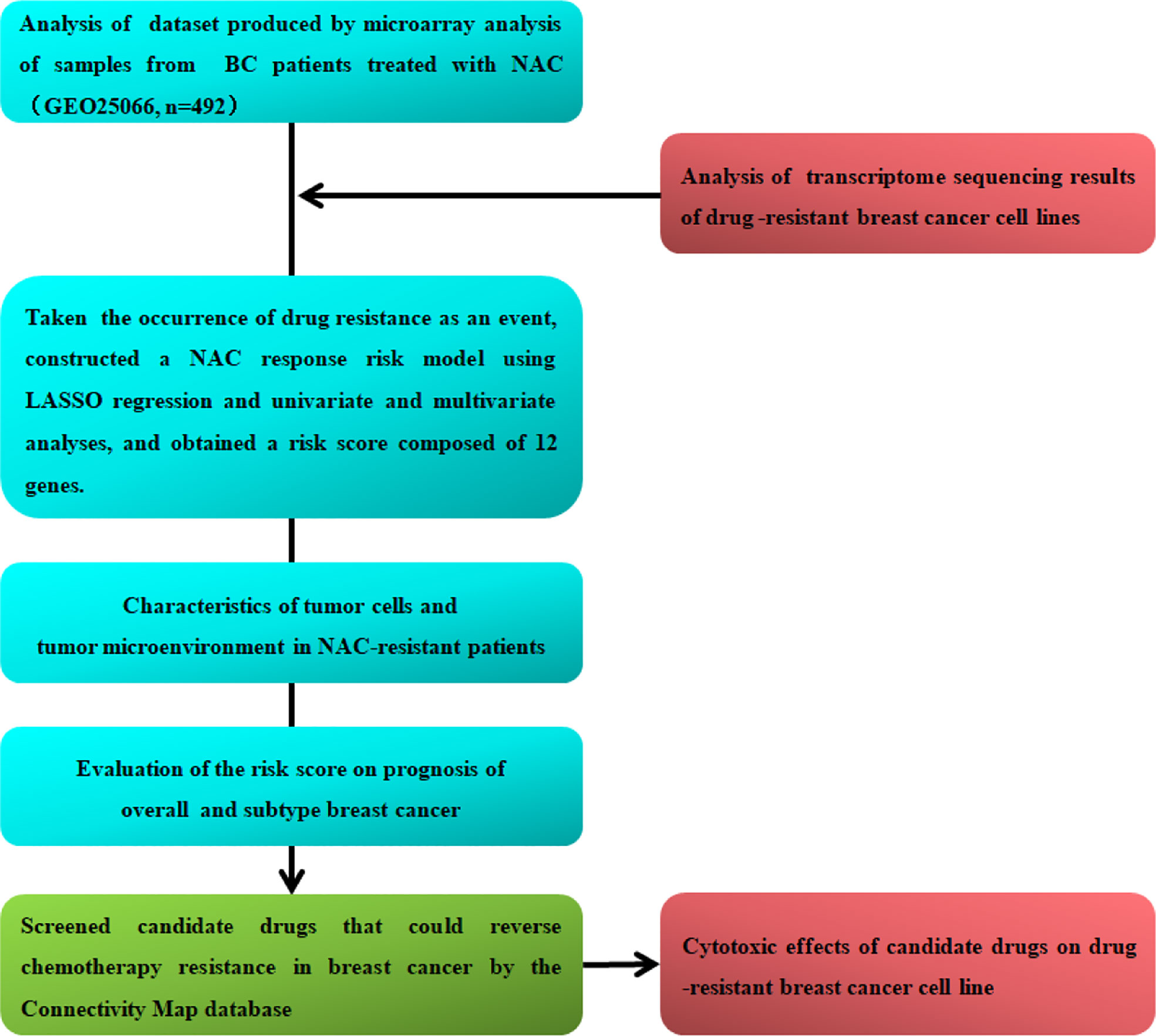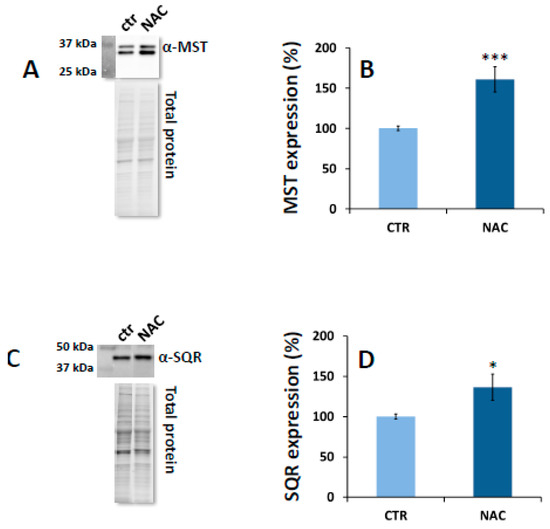
Cells | Free Full-Text | N-Acetylcysteine Serves as Substrate of 3-Mercaptopyruvate Sulfurtransferase and Stimulates Sulfide Metabolism in Colon Cancer Cells
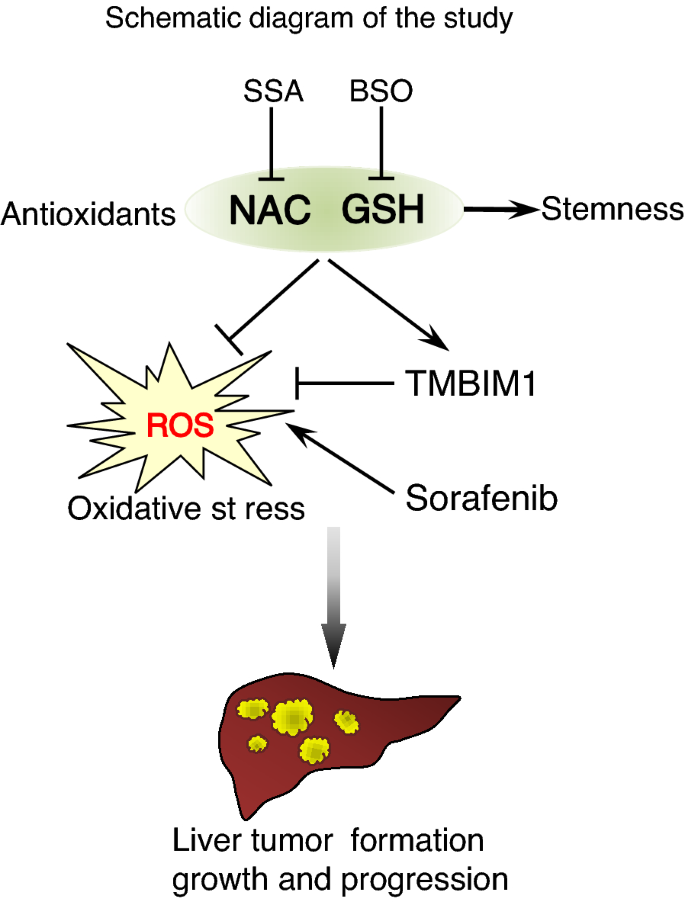
Antioxidant supplements promote tumor formation and growth and confer drug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by reducing intracellular ROS and induction of TMBIM1 | Cell & Bioscience | Full Text

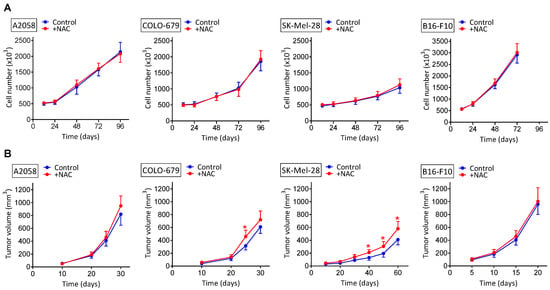
NAC and vitamin E reduce ROS and DNA damage and increase tumor cell... | Download Scientific Diagram

NAC rescues cancer cells from the cytotoxicity induced by combined DHEA... | Download Scientific Diagram

Antioxidants | Free Full-Text | Possible Beneficial Effects of N- Acetylcysteine for Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
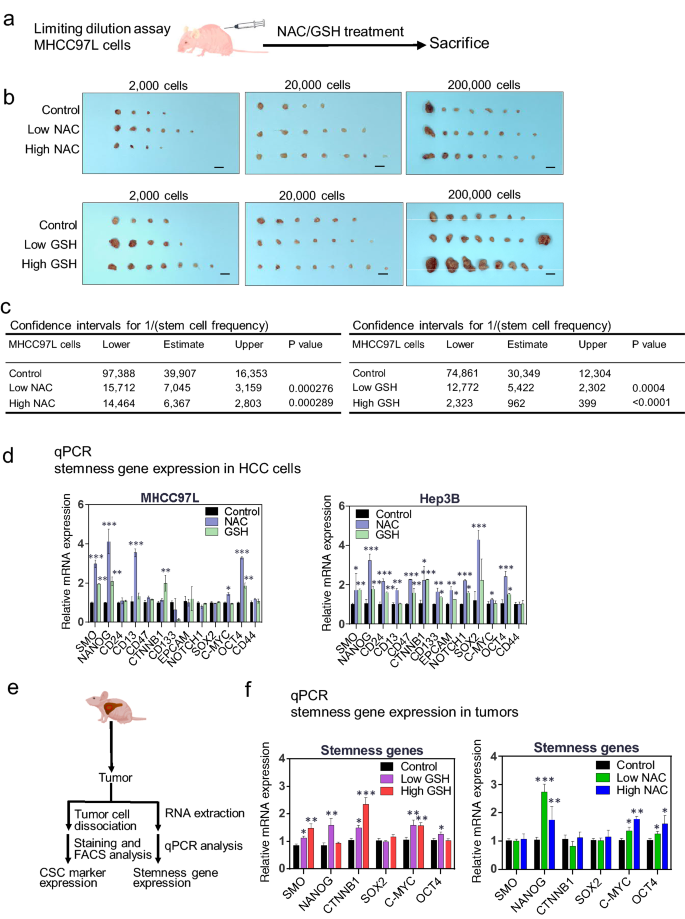
Antioxidant supplements promote tumor formation and growth and confer drug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by reducing intracellular ROS and induction of TMBIM1 | Cell & Bioscience | Full Text
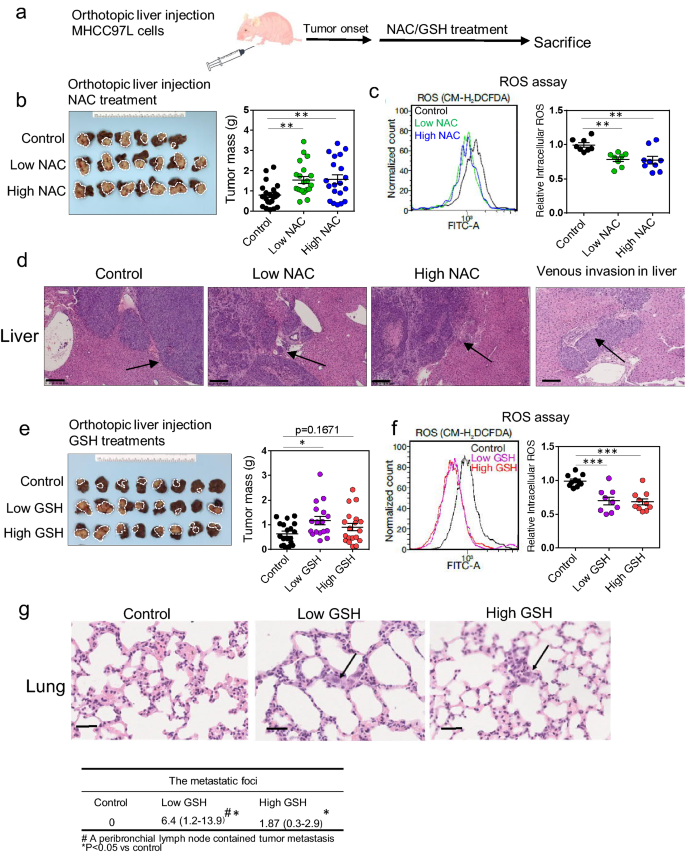
Antioxidant supplements promote tumor formation and growth and confer drug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by reducing intracellular ROS and induction of TMBIM1 | Cell & Bioscience | Full Text
Effects of NAC and GSSG on JS-K-and Taxol-induced apoptosis in prostate... | Download Scientific Diagram

N-Acetyl-l-cysteine Enhances the Effect of Selenium Nanoparticles on Cancer Cytotoxicity by Increasing the Production of Selenium-Induced Reactive Oxygen Species | ACS Omega

N-acetylcysteine (NAC) inhibits cell growth by mediating the EGFR/Akt/HMG box-containing protein 1 (HBP1) signaling pathway in invasive oral cancer. | Semantic Scholar

The paradoxical effect of NAC in isogenic colon cancer cell lines. (a)... | Download Scientific Diagram

Breast Multiparametric MRI for prediction of NAC Response Challenge (BMMR2 Challenge) - The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA) Public Access - Cancer Imaging Archive Wiki
![PDF] Antimetastatic potential of N-acetylcysteine on human prostate cancer cells. | Semantic Scholar PDF] Antimetastatic potential of N-acetylcysteine on human prostate cancer cells. | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/e79c0cab7ee325f5654d8a92a26e4554a97a38ed/3-Figure1-1.png)
PDF] Antimetastatic potential of N-acetylcysteine on human prostate cancer cells. | Semantic Scholar

Pilot study demonstrating metabolic and anti-proliferative effects of in vivo anti-oxidant supplementation with N-Acetylcysteine in Breast Cancer - ScienceDirect

NAC blocks the growth inhibitory effect of CDDO-Me on colorectal cancer... | Download Scientific Diagram
![PDF] Antimetastatic potential of N-acetylcysteine on human prostate cancer cells. | Semantic Scholar PDF] Antimetastatic potential of N-acetylcysteine on human prostate cancer cells. | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/e79c0cab7ee325f5654d8a92a26e4554a97a38ed/4-Figure2-1.png)
PDF] Antimetastatic potential of N-acetylcysteine on human prostate cancer cells. | Semantic Scholar